Implications of the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism for the Iron & Steel sector
On October 1st 2023, the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) became effective. As a measure to limit carbon leakage, the instrument complements the European Emission Trading System (EU ETS) by establishing a carbon price on imported goods that is equivalent to the carbon price on domestically produced goods. CBAM introduces a set of reporting and compliance obligations for importers of goods into the European Union.
Why is CBAM needed?
In a nutshell, CBAM is a policy instrument aiming to reduce the risk of carbon leakage under the EU ETS, the largest carbon pricing scheme worldwide that covers approximately 40% of the EU’s emissions. Carbon leakage refers to the phenomenon where climate policy restricts the competitiveness of domestic manufacturers compared to foreign producers that underly less stringent policies and can produce in a less expensive but environmentally more harmful way. The risk then arises that industry moves from the regulated jurisdiction to countries with lower environmental standards. Climate policy that does not manage carbon leakage could lead to the relocation of emission-intensive manufacturers abroad. Emissions would be exported instead of mitigated, and the domestic economy remains weakened.
Under the EU ETS, regulated entities, that are subject to the risk of carbon leakage, receive emission allowances free of charge conditional on their emission intensity in relation to a sectoral benchmark. This way, the competitive disadvantage of European climate policy is mitigated. The distribution of free allowances is phased out until 2034 and CBAM serves as a substitute to reduce the risk of carbon leakage for EU’s industry from there on.
What is the mechanism & scope of CBAM?
CBAM starts with a transitional period from October 2023 until end of 2025 with only reporting obligations for importers of certain goods. Importers or indirect customs representatives that transfer any CBAM goods into the EU, are obliged to calculate and report the embedded emissions that occur during the production process of CBAM goods and their precursors according to detailed rules.
The definitive period of CBAM starts in 2026. From then onwards, importers must purchase a proportional amount of CBAM certificates. The price of CBAM certificates is closely linked to the price of emission allowances in the EU ETS, momentarily around 85 Euro per ton of CO2e and expected to range between 100 and 150 Euro by 2030. Any carbon price due for the embedded emissions in countries of origin reduces the number of CBAM certificates to be surrendered (cf. figure 1). This mechanism assimilates the carbon price due for foreign and domestic goods that are sold on the EU market. Compared to the system of free allocations, CBAM not only increases the EU ETS revenues (free allocations of emission allowances are phased out), but also incentivizes ambitious carbon prices and industrial decarbonization abroad.
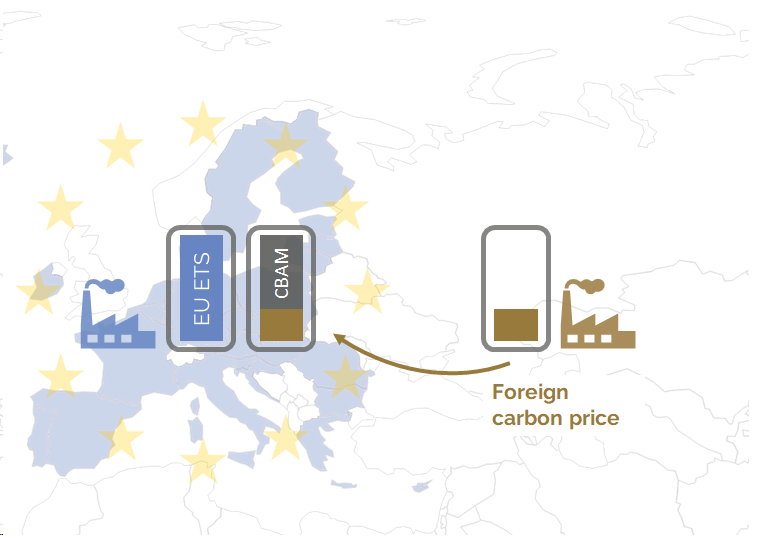
Figure 1 CBAM – basic principle. Source: carboneer.
CBAM currently covers six EU ETS sectors accounting for roughly 50% of emissions in the EU ETS: aluminium, cement, electricity, fertilisers, hydrogen, and iron & steel. For now, in the iron & steel sector, 478 CN goods are combined into 8 aggregated goods categories that share similar production routes, system boundaries and precursors. The CBAM covers mostly emissions of CO2 but includes perfluorocarbons for aluminium products and nitrous oxide for some fertilisers. For the iron & steel sector, only CO2 emissions are relevant.
The European Commission will designate additional products further along the value chain of CBAM goods for potential inclusion in the regulation no later than by the end of 2024. Starting in January 2028 and subsequently every two years, the Commission will evaluate the overall effectiveness of CBAM and deliberate on the potential inclusion of additional sectors within CBAM.
What are the CBAM obligations for importers?
To fulfil their CBAM obligations, importers or indirect customs representatives must register as authorised CBAM declarants prior to the import of CBAM goods into the EU. For each calendar year, regulated companies must calculate the emissions embedded in imports following the methodology set out below and report the results through the CBAM declaration by May 31st in the following year. Within these declarations, the importers may also claim a reduction of CBAM certificates to be surrendered when a carbon price has been effectively paid in the country of origin. The information contained in the CBAM declarations must be validated by third party verifiers that are accredited under the EU ETS regulation. Importers must get access to the CBAM registry, the platform where data on embedded emissions is communicated to authorities and where CBAM certificates are bought, surrendered, and excess certificates are sold back to the authorities.
The obligation to surrender CBAM certificates is phased in until 2034. For the transitional period, no CBAM certificates need to be purchased. Starting with the definitive period in 2026, importers need to surrender CBAM certificates. The number of CBAM certificates to be surrendered, increases proportionally to the phase-out of free allocations in the EU ETS: in 2026 regulated companies have to surrender CBAM certificates for 2.5% of their embedded emissions. This share gradually increases until it reaches 100% in 2034.
How to calculate embedded emissions
The EU defined detailed rules for the calculation of embedded emissions. Generally, CBAM declarants must consider direct emissions from the production process as well as indirect emissions from the generation of energy used in the production process. The CBAM Directive lists some goods (also from the iron & steel sector) for which only direct emissions are to be considered as the production facilities benefit from EU compensation for higher electricity prices due to carbon pricing. For the actual calculation of direct emissions, obliged entities can follow either of the methodologies:
- The calculation-based approach where raw materials and inputs used in production are combined with calculation factors such as net calorific values or emission factors.
- The measurement-based approach where emissions are determined through continuous measurement of flue gas flow and greenhouse gas concentrations in flue gases.
When CBAM declarants lack the required data to perform the calculations they can revert to default values to be used as emissions factors. Default values are to be published by the end of 2023, the EU has however published a first study indicating the differences in emission intensities among the EU and its trading partners for CBAM goods (cf. figure 2).
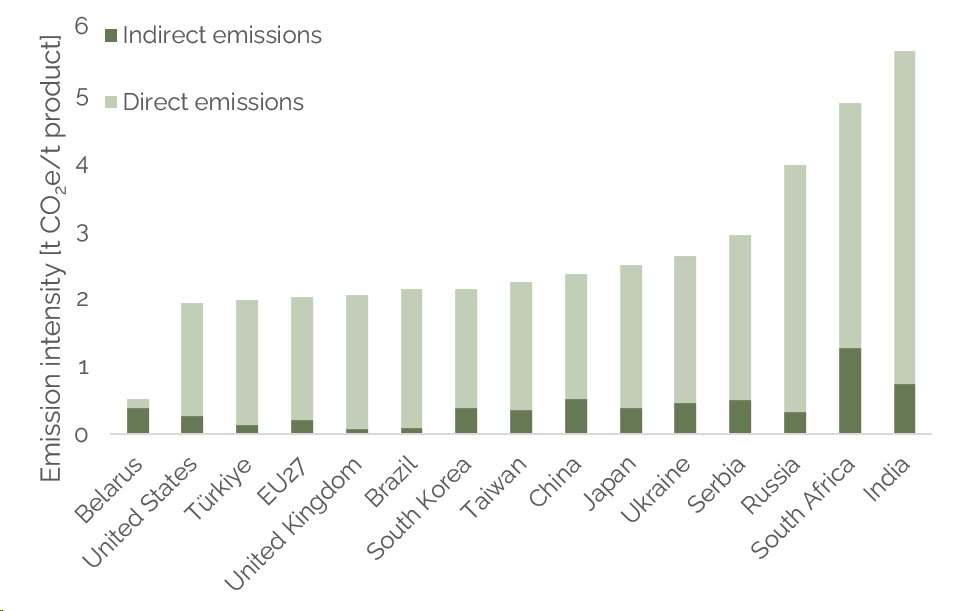
Figure 2 GHG emission intensity for CN code 7217 10 – Wires of non-alloy steel. Value for Belarus is based on the secondary production route. Source: Vidovic et al. (2023).
CBAM declarants can also ask their suppliers to register themselves as an operator located in a third country within the CBAM registry. They may apply above calculation methodology to their output and obtain verification according to EU ETS standards. Suppliers can then disclose the information on embedded emissions to CBAM declarants who in turn may use this information within their CBAM declarations.
Which rules apply in the transitional period?
Acknowledging the challenges posed by the CBAM for declarants, the EU gradually implements the mechanism with a transitional period which started October 1st 2023 and ends December 31st 2025. The transitional period aims to function as a trial and educational phase for all involved parties, including importers, producers, and authorities. Its purpose is to gather valuable data on embedded emissions in order to improve the methodology for the definitive period starting January 1st 2026. CBAM obligations are reduced to reporting during the transitional period (cf. figure 3).
To increase the learnings during the transitional phase, instead of annual CBAM declarations, declarants must submit CBAM reports on a quarterly basis. The first report, covering the embedded emissions from the fourth quarter 2023 is to be submitted by January 31st 2024. The calculation and general reporting requirements are however somewhat eased for the transitional phase: In addition to the calculation methodology described above (EU Method), for the transitional period, two additional methodologies are available:
- Until December 31st 2024, embedded emissions can be determined through third country national systems such as carbon pricing schemes or monitoring systems whose accuracy and coverage is similar to the EU ETS.
- Until July 31st 2024, embedded emissions can be determined using only default values from the EU or elsewhere if calculation methodologies align.
For the transitional phase, all entities must report on both direct and indirect emissions. The exemptions for indirect emissions in the iron & steel sector mentioned above are only valid for the definitive period. Penalties can be imposed in cases where the reporting declarant fails to submit a correct or complete CBAM report or doesn’t rectify errors when initiated, with penalties ranging from EUR 10 to EUR 50 per tonne of unreported emissions.
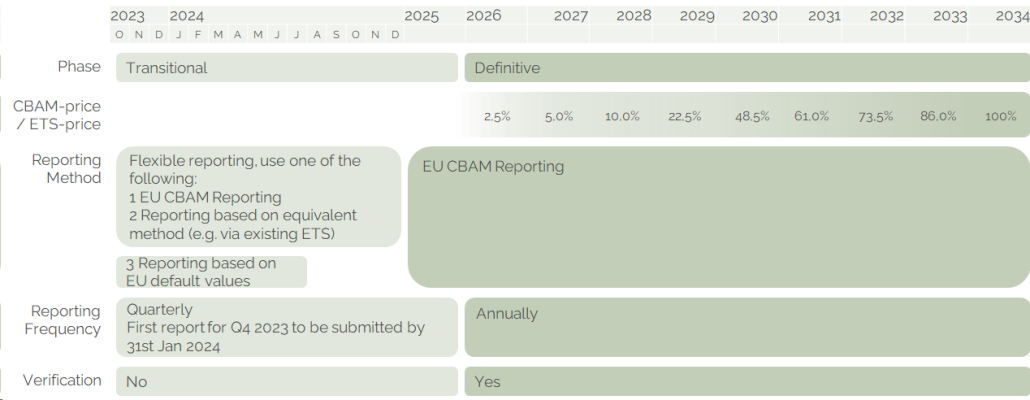
Figure 3 CBAM time schedule. Source: carboneer.
What are the immediate tasks for companies?
The definitive period is two years away, however, here are the preparations companies should conclude at once to comply with the legal obligations of the transitional period and to get a head start for the definitive period:
- Identify which of your imports are subject to CBAM regulations. Engage with suppliers and manufacturers to gather emissions data for imported goods. Collect information on carbon pricing schemes in countries of origin for your CBAM goods.
- Get registered as CBAM declarant or have your indirect customs representative getting registered.
- Get access to the transitional CBAM registry. This is the interface for regulators and regulated entities for the transitional period.
- Learn how to handle the CBAM reporting template published by the EU.
- Establish processes to collect emissions data and set aside personnel capacities to handle CBAM duties.
- Make use of EU ETS allowance price forecast and embedded carbon projections to assess the medium-term economic implications of CBAM regulations on your supply chain and business.
- Understand the implications of CBAM on your supply chain and assess your price and regulatory risk in different countries.
With the introduction of CBAM, emission monitoring and reporting along with carbon pricing plays an ever more important role for non-EU producers and importers. While the emission reporting obligations during the transitional period of CBAM are new to many companies and require comprehensive preparation, regulations on CBAM will evolve during the coming years and should be closely monitored by third country and EU producers as well as traders and importers alike. Details on CBAM implementation rules will for example still be required on the treatment of green electricity procurement through power purchase agreements in third-countries or on updated product lists subject to CBAM obligations. Ultimately, companies require a strategic approach towards these new realities of global trade and decarbonization.
Sources:
Vidovic, D., Marmier, A., Zore, L. and Moya, J., Greenhouse gas emission intensities of the steel, fertilisers, aluminium and cement industries in the EU and its main trading partners, Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg, 2023, doi:10.2760/359533, JRC134682.